If you consider the history of Donald Trump’s public relationship with Vladimir Putin, you won’t be surprised that there’s a fair amount of concern in Ukraine and among Ukraine’s European allies at what might happen when the two meet in Alaska tomorrow for their summit.
While it’ll be their first face-to-face meeting of Trump’s second presidency, the pair has met previously on six occasions and, as we know, spoken fairly frequently over the phone.
The first face-to-face meeting was at the G20 summit in Hamburg in 2017, just months into Trump’s first term. The pair spent two hours of a scheduled 35-minute meeting talking about all things from Syria to North Korea. It was constructive and cordial, they said. Later they talked during a summit dinner in an exchange that was only witnessed by Putin’s interpreter, the nature of which was not reported.
They enjoyed a brief encounter at that year’s Apec conference in Vietnam, sharing a handshake but having no formal discussion.
The following year they met for the now notorious summit in Helsinki, where Putin denied US intelligence reports that Russia had interfered in the 2016 election and Trump said he had no reason to doubt Putin’s word. The two spent two hours closeted with only their interpreters present. Trump’s high spirits were exhibited by a couple of winks he gave the Russian president during their public exchanges.
There was a brief exchange at the G20 summit later that year in Buenos Aires, but this was at the height of the justice department’s investigation into election meddling into Russian election interference. It was a subject Trump returned to when they met at the 2019 G20 summit in Osaka, where Trump seemed to grin as he told Putin: “Don’t meddle in the election.”
As a result, as Stefan Wolff puts in, “expectations are low and anxieties are high” in the run-up to tomorrow’s meeting. Wolff, an expert in international security at the University of Birmingham, sees a number of possible pitfalls for Ukraine in the meeting. Trump has billed the summit as “a feel-out meeting” at which he will get a sense of whether it’s possible to agree a ceasefire. But the US president and his secretary of state, Marco Rubio, have reportedly already sketched out scenarios whereby Putin is offered Ukrainian territory in return for a ceasefire.
The Ukrainian president won’t be there, of course. But he has already said that he won’t accept a deal which imposes a giveaway of Ukrainian territory (which would, in any case, violate his country’s constitution). Wolff believes this would give Putin the opportunity to paint Zelensky as the problem – the man denying the US president his Nobel peace prize.
On the other hand is the possibility that Trump will persuade Putin to agree to a three-way with Zelensky but without other European leaders. Wolff believes this brings with it the danger that Putin (who as a longtime Soviet intelligence officer would have plenty of experience at this sort of thing) would be able to manipulate the meeting into the sort of blow-up between Trump and Zelensky we saw in their disastrous meeting at the White House in February.
Read more: Trump's Alaska summit with Russia is shaping up to be the most important of his second presidency
These are clearly all concerns shared by Ukraine’s European allies, so much so that they convened an emergency virtual conference on August 13. Zelensky, German chancellor Friedrich Merz and an array of other European leaders warned Trump and his vice-president, J.D. Vance, that Ukrainian and European interests must be protected at the summit.
The main worry, writes Michelle Bentley, a professor of international relations at Royal Holloway University of London, will be that while Putin’s position is clear, Trump’s is not. Putin wants a deal that recognises Russian ownership of Crimea and the various provinces in Ukraine’s east that his military already occupies, including land it has not managed to take by force. He wants to prevent Ukraine joining Nato and wants the country to demilitarise.
Trump, by contrast, wants to do a deal. Partly because he has said he will do one. And partly because there is economic benefit to be had for the US in repairing relations with Russia. Bentley also worries that the US president has a track record of support for the Russian president and the mere fact that the pair are getting together for a summit on equal terms effectively brings to an end the years of Russia’s diplomatic isolation in the west.
Read more: Will Trump-Putin summit leave Ukraine and Europe out in the cold?
Let’s make a deal
What will also be worrying Kyiv and its allies is Trump’s singular foreign policy style, which is notably transactional. It may be the US president’s background in real estate asserting itself (and it’s no coincidence that his envoy to Russia and at times to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, Steve Witkoff, is from a similar background).
Just recently, Trump hosted the leaders of Armenia and Azerbaijan in the Oval Office for a meeting at which they signed a deal to end the decades of conflict between their two countries. Integral to the deal is the development of a new corridor through Armenia to link Azerbaijan with its enclave of Nakhchivan. Previously known as the Zangezur corridor, the link will have the name the Trump Route for International Peace and Prosperity.
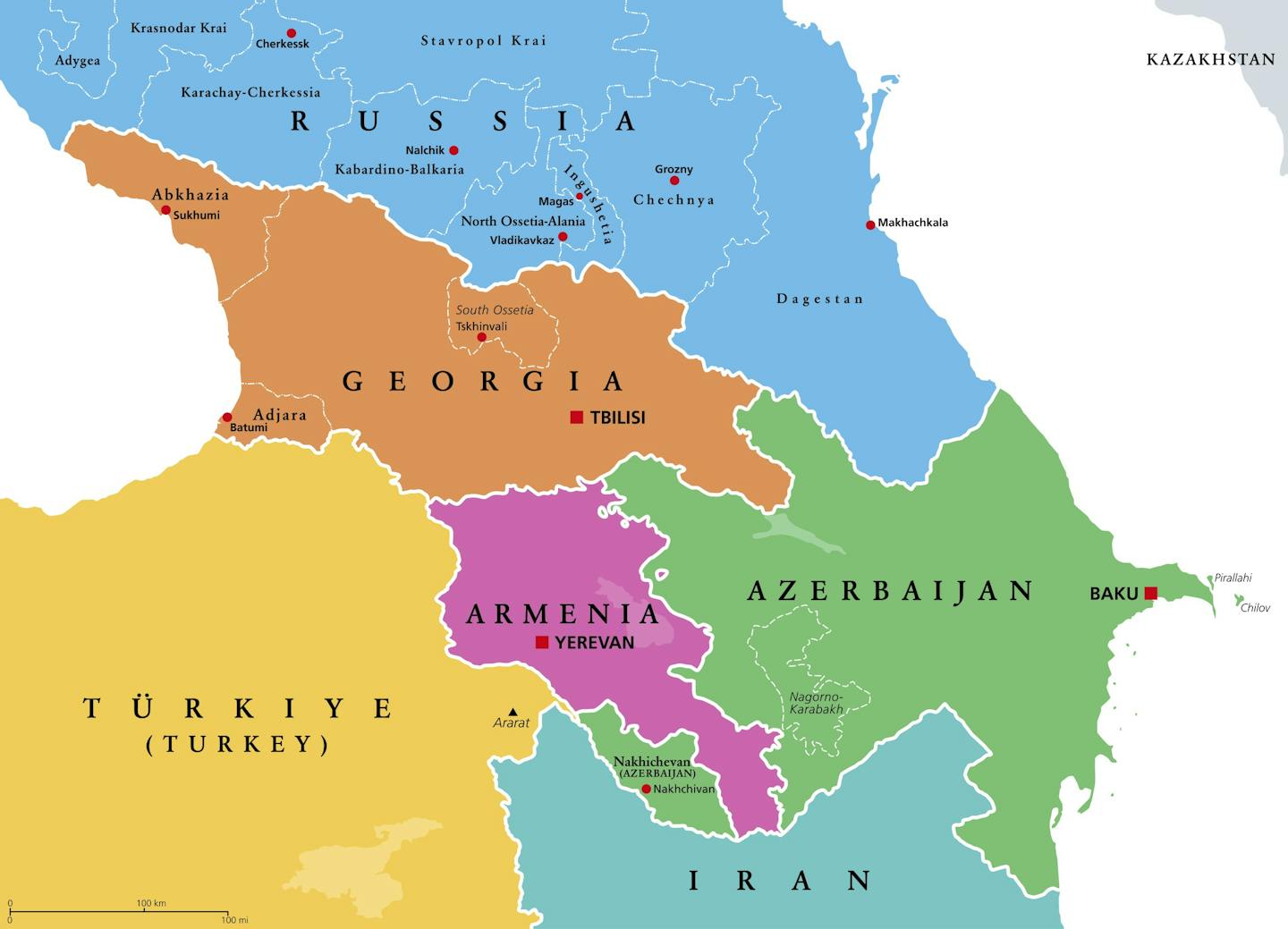
Trump is by no means the first US president to link commerce or economic incentives with diplomacy, writes Patrick Shea, an expert in international relations and global governance at the University of Glasgow. But Trump’s style is somewhat different, he writes. The president’s deals often skirt dangerously close to the wind in terms of international law, the recent tariff policies being an example.
Read more: US presidents have always used transactional foreign policy – but Trump does it differently
Foreign governments, meanwhile, are first learning that such sweeteners can be effective in dealing with this administration. As is flattery. So it’s notable that, following Trump’s warning to Putin to get serious about doing a deal, the Russian president has been fulsome in his praise of Trump’s “sincere efforts” to bring about peace in Ukraine.
Trump has made a big fuss about Putin coming to see him in Alaska, a US state. He sees that as courtesy on the part of the Russian leader. But there are many who think holding the summit in a territory that one belonged to Russia means the whole meeting has a subtext that territorial sovereignty is not absolute and that it does change hands from time to time. Here’s a brief history of Alaska from William L. Iggiagruk Hensley of the University of Alaska Anchorage, a former member of the state legislature.
Read more: Trump-Putin meeting in Alaska is a reminder that the 49th state was once a Russian territory
Peace in our time?
A major international summit, where an aggressor is threatening to invade another country with the prospect of a major European war? We’ve been here before. The summit was at Munich in September 1938, the aggressor was Germany and the country at threat was Czechoslovakia. And like the impending Alaska summit where Ukraine has not been invited, when the British and French leaders visited Adolf Hitler to talk peace, Czechoslovakia was not in the room.
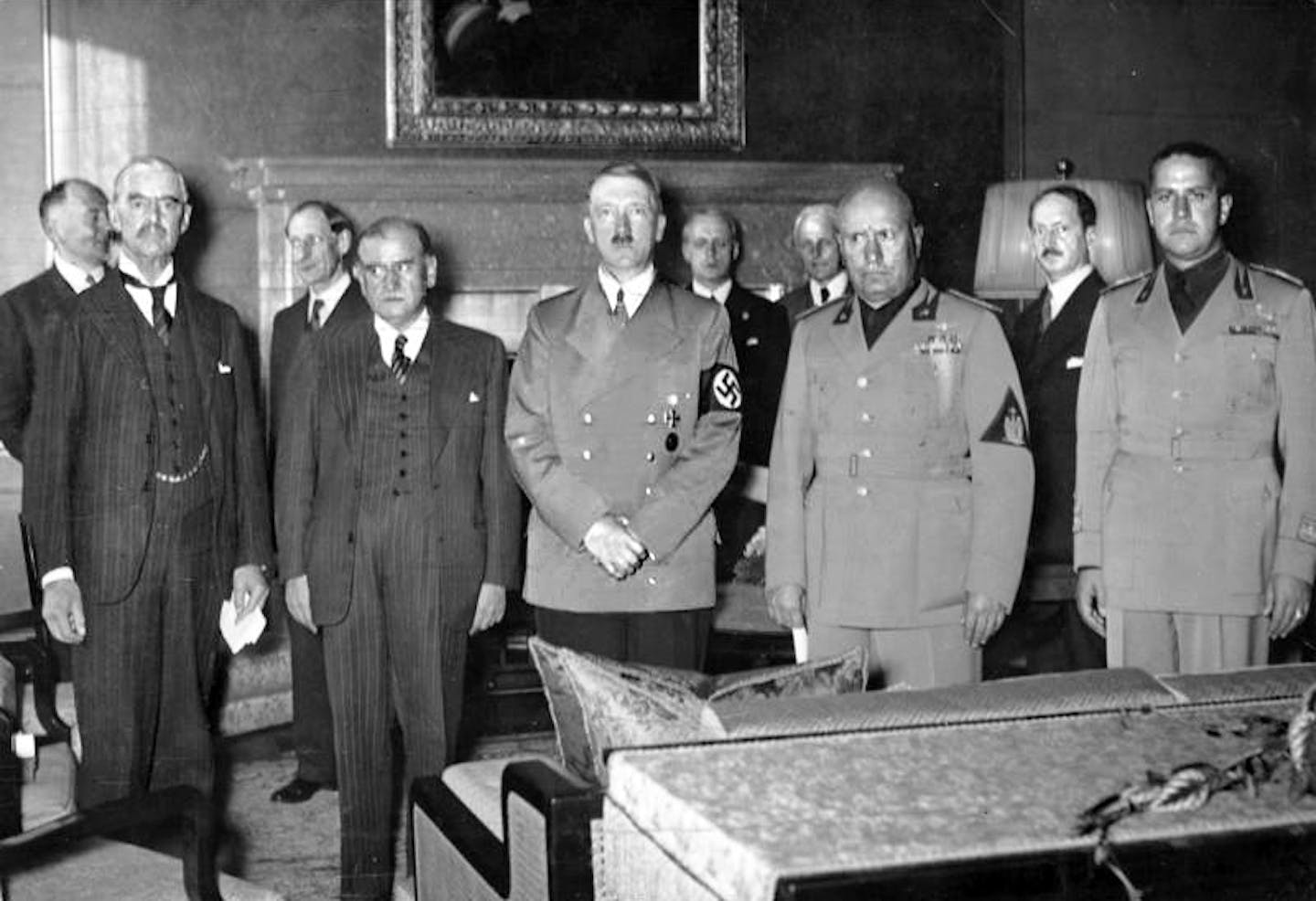

The example of Munich 1938 doesn’t fill one with a great deal of confidence for Ukraine’s future security, writes Tim Luckhurst, a historian of the second world war.
Luckhurst recounts the events leading up to Munich, at which British prime minister, Neville Chamberlain, and his French counterpart, Édouard Daladier, agreed that Germany would be allowed to annex the Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia, with no involvement of the Czech leader, Edvard Beneš.
It would be “peace in our time”, boasted Chamberlain. It wasn’t even peace for a year.
Read more: Alaska summit: why Donald Trump should heed the lessons of Munich 1938 when he meets Putin
Meanwhile in Israel
To Israel, where this weekend there is likely to be one of the biggest mass protests and general strikes in the country’s history on Sunday August 17. Huge numbers of people are expected to turn out in protest at the Netanyahu government’s failure to secure the release of the remaining October 7 hostages and the prime minister’s plan to launch a fresh offensive to take and occupy Gaza city despite the risk to the remaining hostages’ lives.
Benjamin Netanyahu’s position as prime minister is looking far from secure. The next election is due in October 2026, but John Strawson – an expert in Israeli politics at the University of East London – believes a new poll may be held much sooner than that.
Netanyahu’s parliamentary coalition is becoming more shaky as his ultra-orthodox supporters quit the government in protest at the government’s decision to scrap the exemption from conscription enjoyed by orthodox Israeli students.
But whether this will bring any relief to Palestinians is doubtful. Recent polling suggests that while there is huge support for an end to the war, this doesn’t translate into public backing for a two-state solution.
Read more: Israel's opposition: against Benjamin Netanyahu but not yet for peace with the Palestinians
Sign up to receive our weekly World Affairs Briefing newsletter from The Conversation UK. Every Thursday we’ll bring you expert analysis of the big stories in international relations.
![]()


 The Conversation
The Conversation
 America News
America News Associated Press US News
Associated Press US News Associated Press Top News
Associated Press Top News CBS4 Miami
CBS4 Miami Associated Press US and World News Video
Associated Press US and World News Video Raw Story
Raw Story Blaze Media
Blaze Media